Immunology for gene transfer
Immunology of gene transfer after AAV vector delivery
Recombinant adeno-associated viruses (rAAVs) are considered efficient and successful viral vectors for the treatment of inherited disorders. However, translation from animal models to patients has shown limits imposed by the host immune system characterized by the initiation of humoral and cellular immune responses to the vector and/or to the transgene. These immune responses might prevent transgene expression in case of anti-AAV pre-existing immunity but also result in gene transfer failure by clearance of transduced cells.
Our lab is dedicated to the understanding of anti-capsid and anti-transgene immune responses in animal models and humans.
Our research is focused on three related areas:
Studying the interactions between the AAV vector and immune cells
Innate sensing of AAV plays a key role in the initiation of an adaptive immune response mediated by CD8+ T cells. While interaction of the recombinant viral genome with the TLR9/MyD88 pathway has been described, interaction between AAV vectors and immune cells still needs investigation. A particular interest is given to antigen-presenting cells.
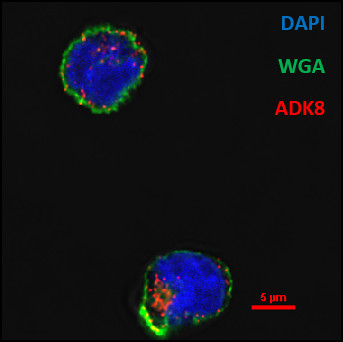
Visualization of pDC (Gen2.2 cell line) transduction by rAAV8
Understanding and characterizing anti-transgene immunity and pre-existing anti-AAV immunity
Recombinant AAV administration in presence of natural pre-existing anti-AAV T cell response can lead to reactivation of these cells and eventually to toxicity in humans. To characterize these cells and study their impact on gene transfer efficiency, we develop sensitive assays such as ELISpot or positive population enrichment using tetramers to detect them in animal models and humans.
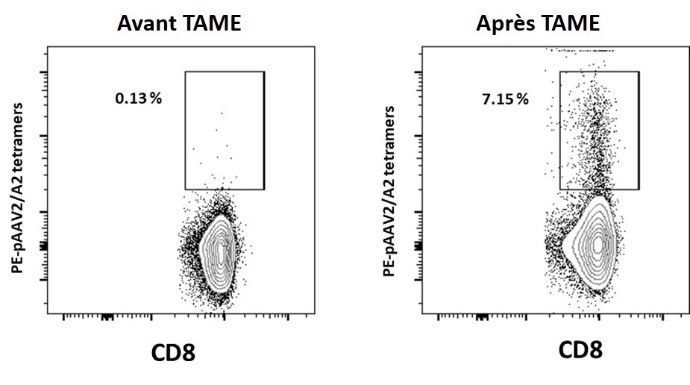
Detection of AAV-specific CD8 T cells pre and post tetramer enrichment
Developing new strategies to circumvent anti-transgene and anti-capsid immunity
The understanding of immune response initiation and the development of reliable models mimicking immune responses observed in patients will help establish new immune modulatory strategies. These strategies include but are not limited to
- insertion of DNA-immunomodulatory sequences in rAAV viral genome to modulate innate immune responses and
- development of targeted tolerogenic strategies to modulate anti-AAV and anti-transgene cellular immunity
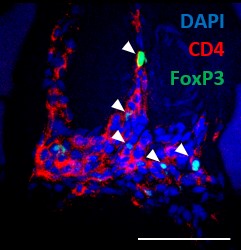
Muscle-infiltrated Tregs after rAAV8 delivery
Oumeya ADJALI, M.D., Ph.D., DR2 INSERM, Head of the Lab
Virginie PICHARD, Ph.D, Senior Scientist
Gwladys GERNOUX, Ph.D, Senior Scientist
Allan AVENEL, Ph.D. student
Célia COUZINIE, Engineer, GTI Operational Manager
Mickaël GUILBAUD, Engineer, MSc, Research Scientist
Amandine MARTIN, Engineer, MSc, Research Associate
Nicolas JAULIN, Technician, Research Associate
Johanne LE DUFF, Technician, Research Associate
Laure CARRE, Ph.D. student
Manon LUCAS, Ph.D. student
Manon SCHMITT, Ph.D. student